Web コンテンツ・ビューアー
Web コンテンツ・ビューアー
Intelligent Noise Reduction
The Future Generation of Imaging
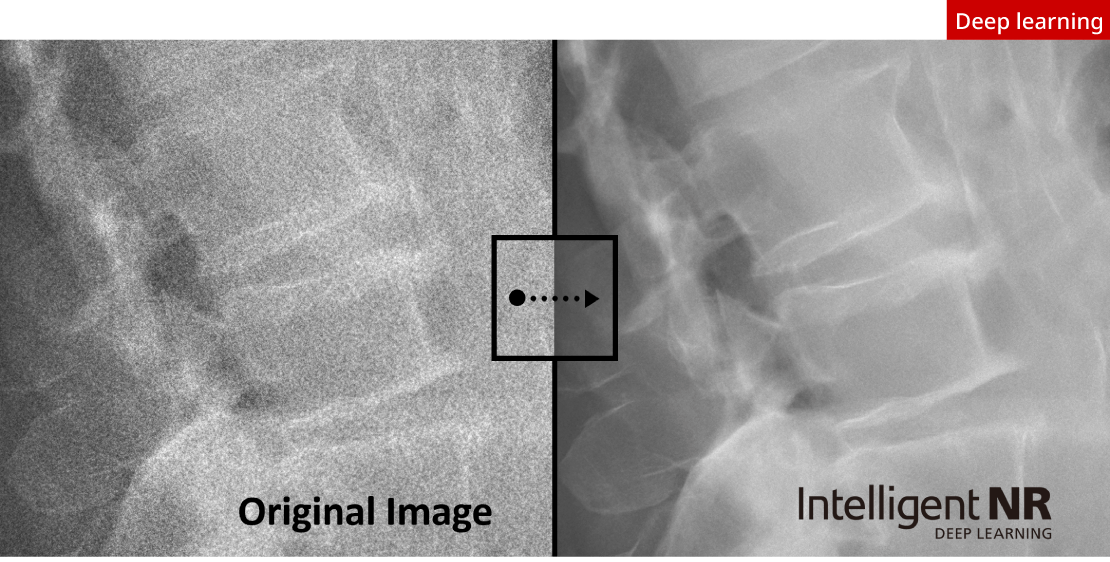
Intelligent Noise Reduction (Intelligent NR)
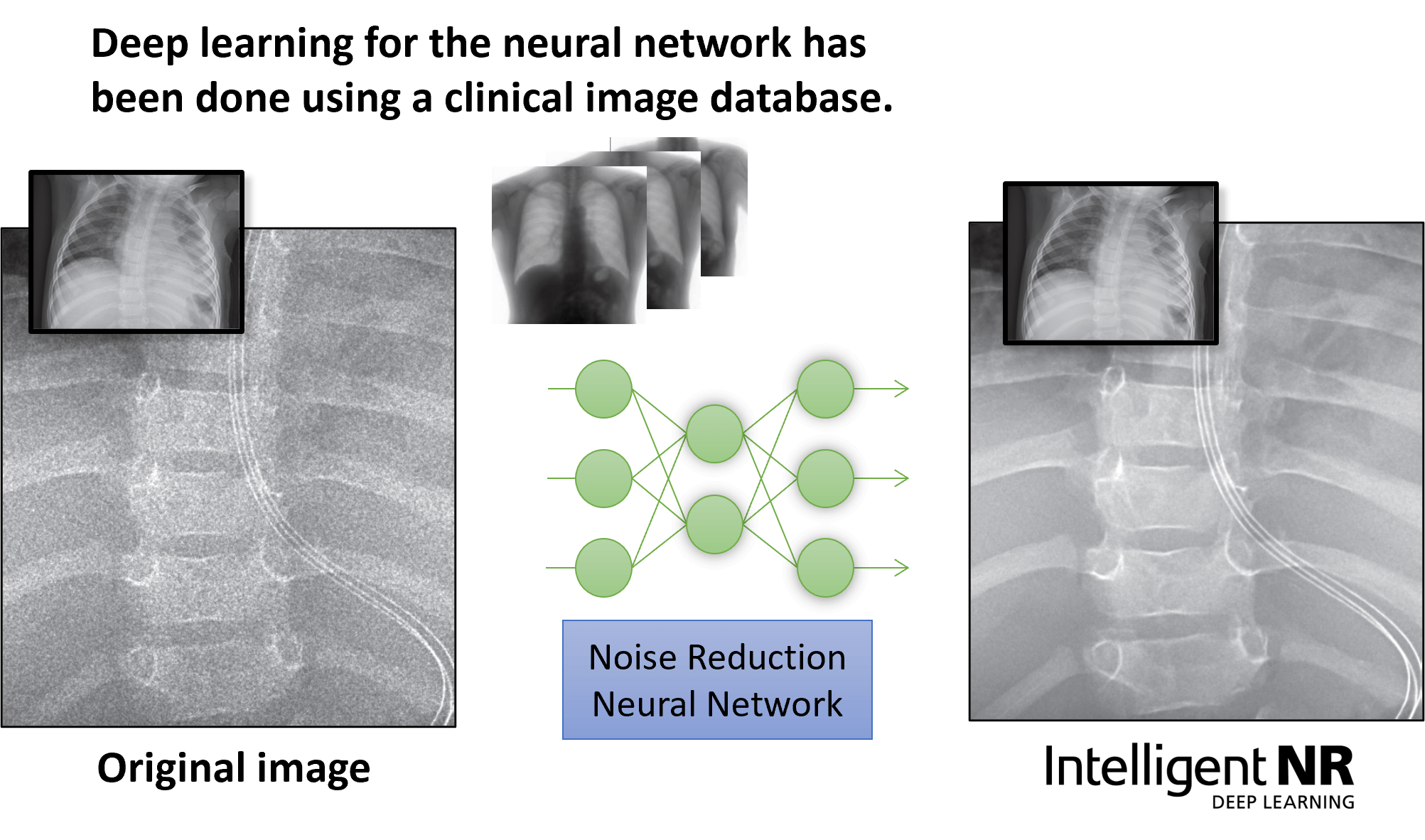
Canon’s new AI image processing uses a pre-determined model which has been trained by deep learning on noise characteristics in X-ray images from a clinical image database.
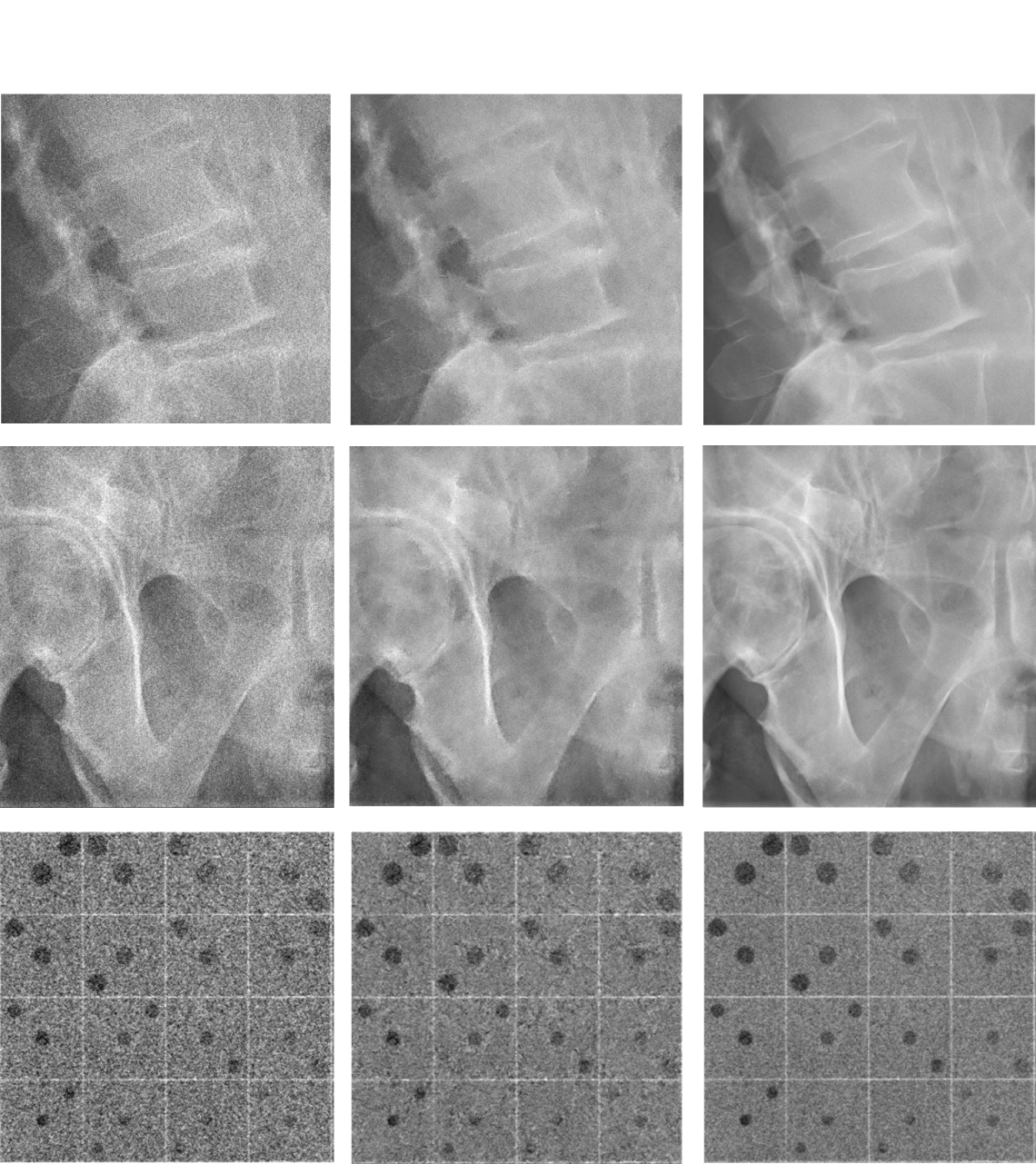
Efficacy of Intelligent NR
- Superior quality diagnostic images
Intelligent NR is a substantial step up from conventional noise reduction. Intelligent NR will provide radiologists high-quality diagnostic images containing significantly less grainy noise with no noticeable loss of detail. This should make improved diagnosis possible for their patients.
Intelligent NR makes it possible to reduce the noise content without losing the fine details of the anatomy, even in low dose regions. For this reason, it is superior to conventional noise reduction. Intelligent NR results in an optimal diagnostic environment, especially for infants and pediatric patients where dose is a prevailing concern. But the image improvement will benefit all patients and exam types by providing superior images even in inherently noisy conditions such as the dense anatomy of the abdomen. With Intelligent NR, there is the potential for significant dose reduction while retaining equivalent image quality (noise content).
Collaborative Research
In collaborative research with St. Marianna University School of Medicine Hospital (Japan), the hospital reported Intelligent NR shows a higher visibility than conventional NR and that Intelligent NR should be useful with almost no texture distortion. Compared to conventional NR, the results suggest that using Intelligent NR should enable the acquisition of better images at lower doses.
- Visible Results
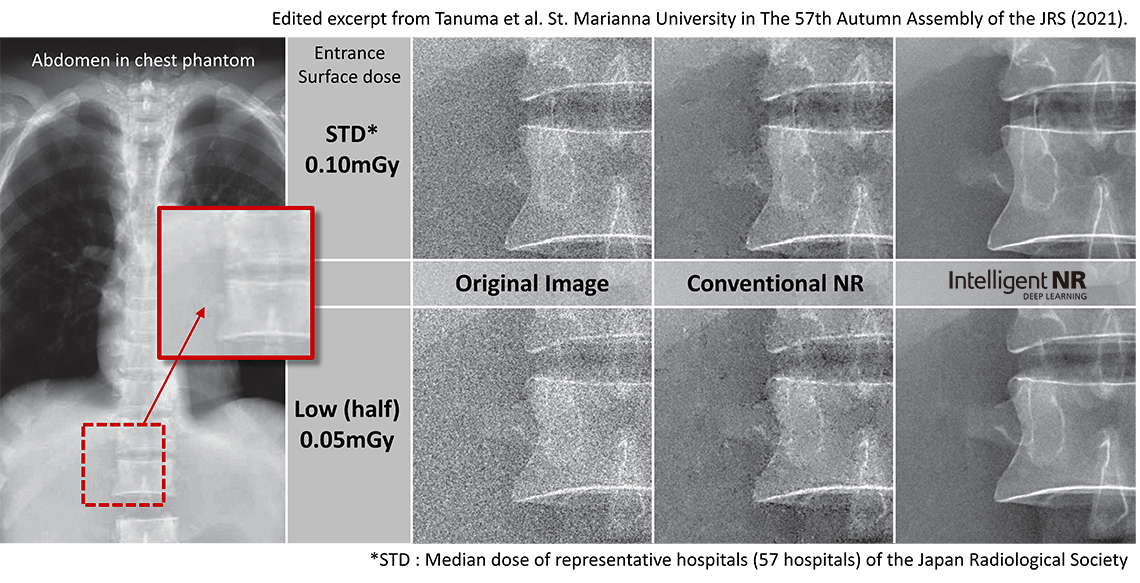
Low (half) dose Intelligent NR image has less graininess than standard dose Conventional NR image in this study.
*Intelligent NR is available with the following Canon detectors CXDI-710CW, 810CW, 410CW, 720CW, 820CW, 420CW, and 420CF.
Adding the option to existing systems, may require additional computer hardware.
†† Specifications subject to change without notice.
Dayton Children’s Hospital (United States) evaluated the capabilities of Intelligent NR in relation to standard and reduced dose pediatric digital radiographs. A total of 1251 digital radiographs (abdomen, extremities, spine, chest and head/shoulder/pelvis/hip) were gathered from 649 pediatric patients at Dayton Children’s Hospital and evaluated across three dose levels: standard dose, 20–25% reduction, and 40–50% reduction. The results suggest Intelligent NR is effective and assists radiologists in diagnostic imaging.
Intelligent NR vs Conventional NR
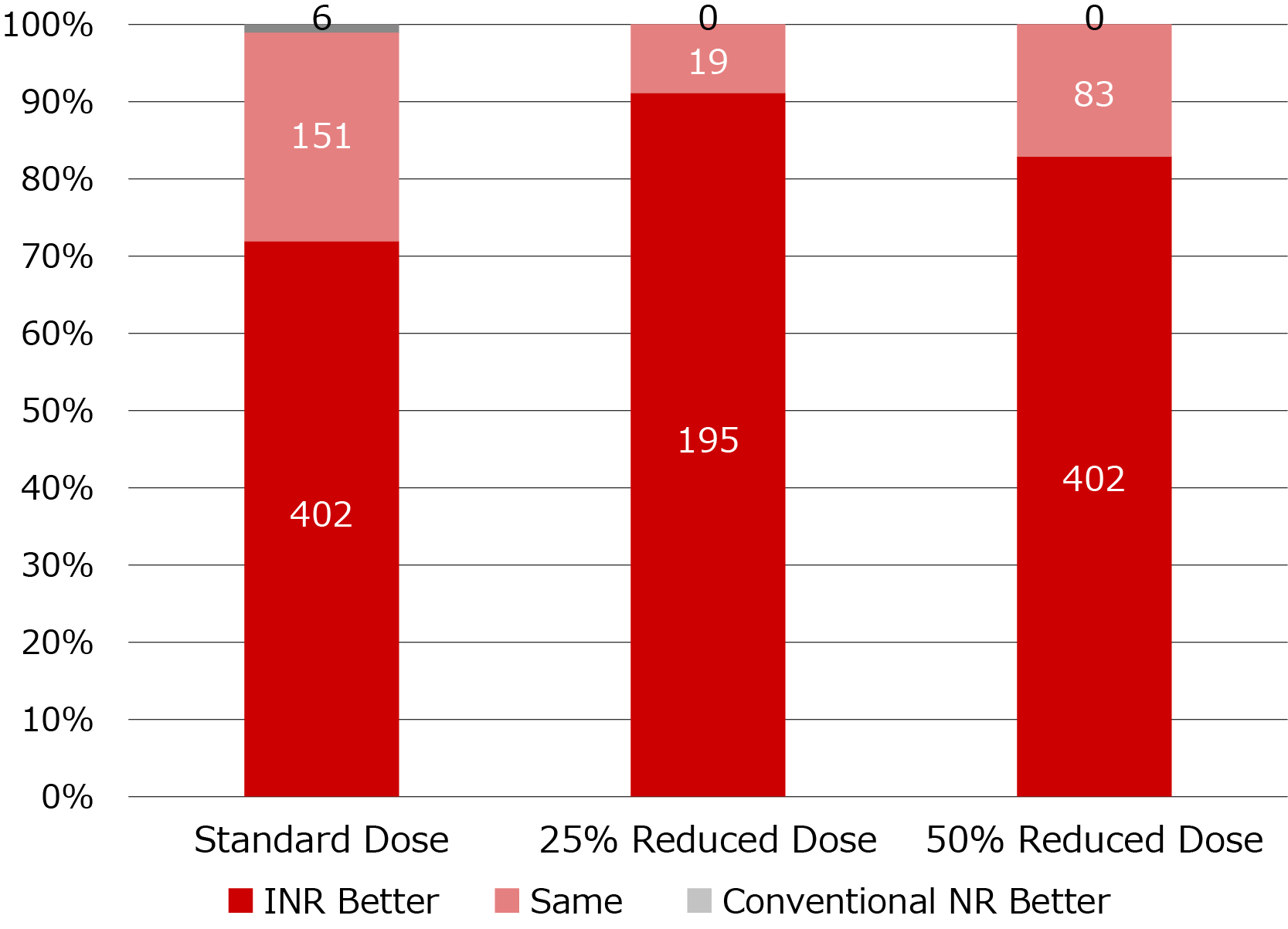
“The Canon DR system with the Intelligent Noise Reduction has produced images with lower noise content at a lower dose with no visible loss in image quality. This has allowed us to use doses that are 50% less than what we had been using in that room.”
Dr. Elizabeth Ey, Chief Radiologist and Radiation Safety Officer in Dayton Children’s Hospital
Literature
-
White papers
Intelligent Noise Reduction: Seeing Through the Noise with Deep Learning Image Processing
Josh Johnson (MS)
An Analysis of Canon Intelligent Noise Reduction Processing Applied to Pediatric Digital Radiographs
Jonah Ice and Selena Yao
-
Research Papers /Journal Articles
Fujikawa et al., Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, St. Marianna University School of Medicine, Japan, 2025
Japanese Journal of Radiology
DOI: 10.1007/s11604-025-01887-2 | CC BY 4.0Hultenmo et al., Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Sweden, 2025
Pediatric Radiology
DOI: 10.1007/s00247-025-06251-0 | CC BY 4.0Mori et al., Department of Radiological Technology, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Japan, 2025
Radiography
DOI: 10.1016/j.radi.2025.102958 | CC BY 4.0Ode et al., Department of Radiology, St. Marianna University School of Medicine, Japan, 2025
Japanese Journal of Radiology
DOI: 10.1007/s11604-025-01775-9 | CC BY 4.0How does intelligent noise reduction software influence the image quality in pelvic digital radiography; a phantom study
Hussner et al., Health Sciences Research Centre, Radiography education, UCL University College, Odense, Denmark, 2024
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmir.2024.101814